Primary Angioplasty in Vijayawada
What Is Primary Angioplasty?
To restore blood flow to a blocked artery the Primary angioplasty is a special case of immediate or direct angioplasty. Angioplasty can also be performed after thrombolytic therapy, either as soon as possible, a procedure called facilitated angioplasty, or a bit later in the post-MI period.
The procedure which treats blockages within the coronary arteries and improves blood flow to the heart is known as Primary angioplasty, also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Your heart’s arteries can become blocked or narrowed from a buildup of cholesterol, cells or other substances (plaque). This can reduce blood flow to heart and cause chest discomfort. Sometimes a blood clot can suddenly form or get worse and completely block blood flow, leading to a heart attack.
Heart Angioplasty in Vijayawada opens blocked arteries and restores normal blood flow to your heart muscle. It is not major surgery. It is done by threading a catheter (thin tube) through a small puncture in a leg or arm artery to the heart. The blocked artery is opened by inflating a tiny balloon in it.
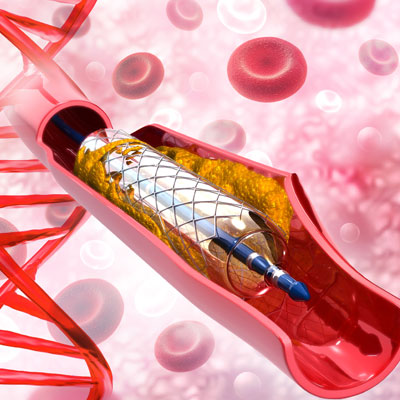
- Primary angioplasty in Vijayawada involves stretching any narrowed areas of the coronary arteries using a balloon which is attached to a thin catheter (tube). Like an angiogram, the catheter is inserted, under local anaesthetic, into a main artery in the upper leg or lower arm and then passed gently into the aorta (the large artery which supplies the heart muscle with its own blood supply).
- The balloon, at the tip of the catheter, is blown up at the narrowed area(s) of the artery; this forces the artery open and widens it.
- In the majority of cases a metal stent will also be placed in the artery. A stent is a cylinder of metal mesh which acts like a scaffold to keep the artery open and prevent the artery narrowing again. The artery heals around the stent making it a permanent part of the artery. You will not be aware that it is there.
- If you have a stent, you will need to take certain ant platelet medicines to help reduce the risk of blood clots forming around the stent.
- Sometimes stents can be used which slowly release medicines, directly to the narrowed area, to help prevent the problem recurring. These are called drug-eluting stents and are used when the risk of re-narrowing is high.
Why do I need it?
People with blockages in their heart arteries may need angioplasty if they are having lots of discomfort in their chest, or if their blockages put them at risk of a heart attack or of dying.
How is it done?
- When numbs a spoton groin or arm and inserts a small tube (catheter) into an artery.
- The catheter is threaded through the arterial system until it gets into a coronary (heart) artery at best heart stenting hospitals in Vijayawada.
- Watching on a special X-ray screen, the doctor moves the catheter into the artery. Next, a very thin wire is threaded through the catheter and across the blockage. Over this wire, a catheter with a thin, expandable balloon on the end is passed to the blockage.
- The balloon is inflated. It pushes plaque to the side and stretches the artery open, so blood can flow more easily. This may be done more than once.
- In many people a collapsed wire mesh tube (stent) mounted on a special balloon, is moved over the wire to the blocked area.
- As the balloon is inflated, it opens the stent against the artery walls. The stent locks in this position and helps keep the artery open.
- The balloon and catheters are taken out. Now the artery has been opened, and your heart will get the blood it needs.
Visit Best heart hospitals in Vijayawada for asdpda treatment.





